Why Can’t I See My RISASection Shapes in the Shape Database?
When using RISA Integration between RISASection and RISA-3D, RISA-2D and/or RISAFloor, there are a few common mistakes that people make when...
Steel
Wood
Concrete
Education
RISA-3D
RISAFloor
RISAConnection
ADAPT-Builder
RISACalc
RISAFoundation
ADAPT-PT/RC
RISASection
RISA-2D
ADAPT-Felt
Link Utilities

Try the Complete RISA Suite for
10 Days FREE
Training
Webinars
Reach an Engineer
Tips & Tricks
Design Codes
Case Studies
New Features
Cloud Licensing

RISA Education

Video Library
Downloads
Licensing Support
Customer Portal
Product Documentation
System Requirements
Specifications
Online Help
Get Support
Contact
Careers
Employee Spotlight
Nemetschek
License Agreement
Privacy Policy
Open BIM
Partners

About Us
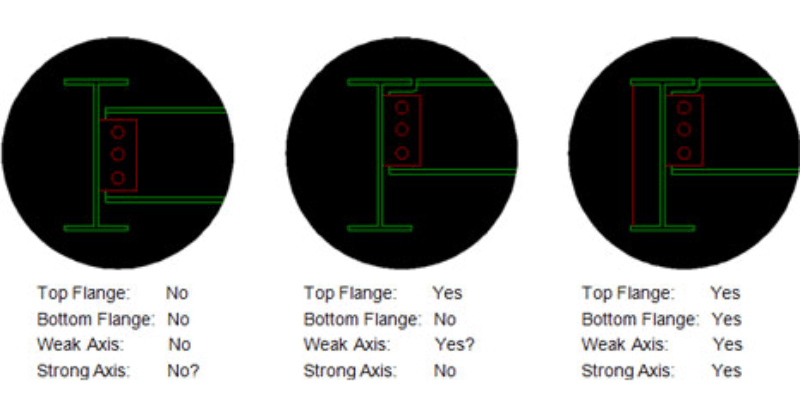
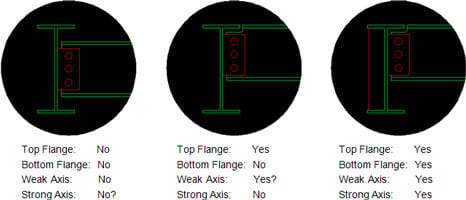
There are four different values for Unbraced lengths in RISA-3D, RISA-2D and RISAFloor. Two are for axial calculations and two are for bending calculations.
Lb is used to determine the unbraced length for axial forces. This is what is used to calculate the KL/r value. The two different directions represent the weak or strong axis of the member. For symmetrical shapes, the yy direction is the weak axis and the zz direction is the strong axis.
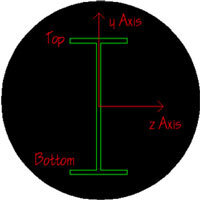
Lcomp is used to determine the unbraced length for bending forces. The top and bottom categories represent the top and bottom of the member. To determine the “top” of the member, turn on the Member local axes in your Plot Options. The positive local y axis points to the “top” of the member.
The connection type determines what values should be used for each of the four un-braced length entries. However, the same connection type doesn’t necessarily mean that the unbraced length values are the same. This varies drastically depending upon the depth of the framing members. The appropriate un-braced values is really an engineering judgment for the design engineer.
When using RISA Integration between RISASection and RISA-3D, RISA-2D and/or RISAFloor, there are a few common mistakes that people make when...

Members (beams, columns, braces, etc.) are defined in RISA by an I-Node and a J-Node. While you and I see a beam occupying physical space...
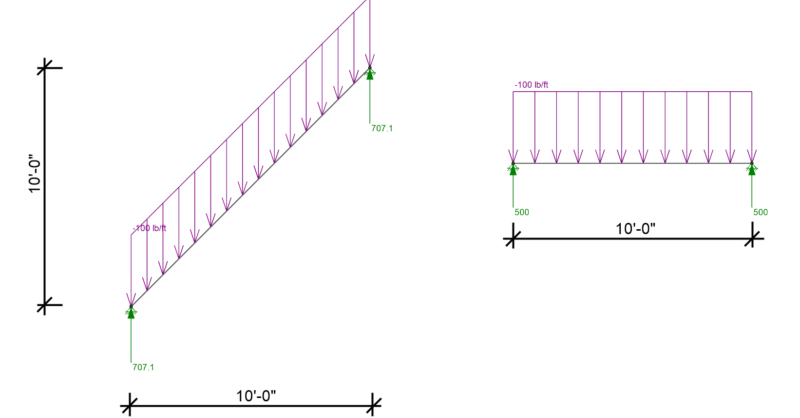
RISA-3D, RISA-2D and RISAFloor have the capability to project distributed and area loads onto members. Consider the case of snow load on two...