What does the Include Structure Weight Checkbox Do for Seismic Loads?
In the Seismic Loads dialog there is a checkbox for “Include structure weight in base shear”.
Steel
Wood
Concrete
Education
RISA-3D
RISAFloor
RISAConnection
ADAPT-Builder
RISACalc
RISAFoundation
ADAPT-PT/RC
RISASection
RISA-2D
ADAPT-Felt
Link Utilities

Try the Complete RISA Suite for
10 Days FREE
Training
Webinars
Reach an Engineer
Tips & Tricks
Design Codes
Case Studies
New Features
Cloud Licensing

RISA Education

Video Library
Downloads
Licensing Support
Customer Portal
Product Documentation
System Requirements
Specifications
Online Help
Get Support
Contact
Careers
Employee Spotlight
Nemetschek
License Agreement
Privacy Policy
Open BIM
Partners

About Us
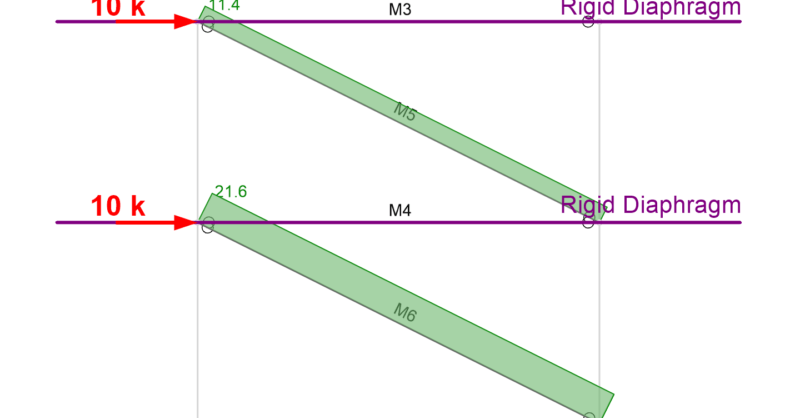
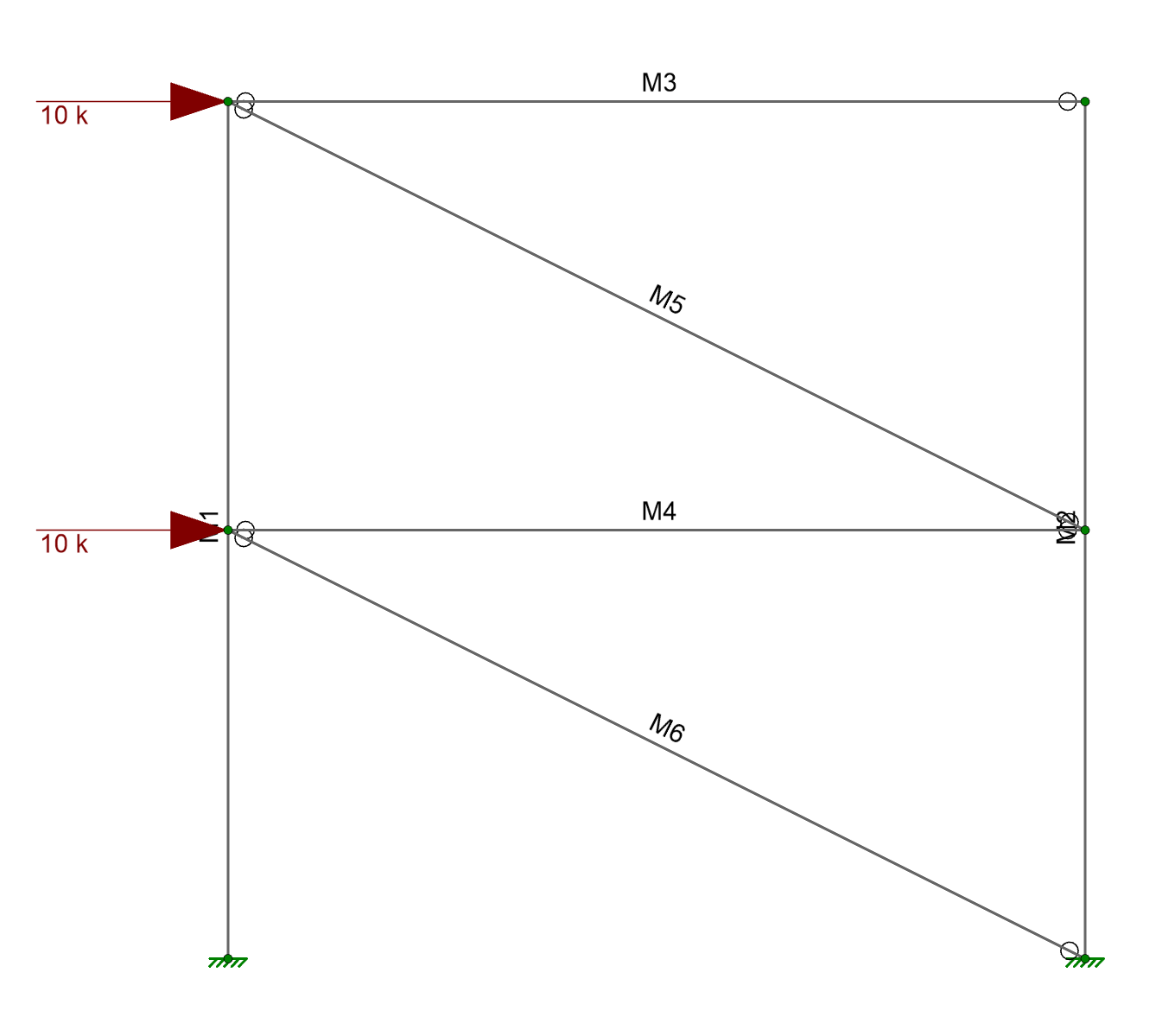
The beams in a lateral force resisting system, such as a braced frame or moment frame, typically carry a significant axial force. In the example below (with no diaphragms) the beam (M4) carries a significant axial tension.
The axial force diagrams show that the beam (M4) is carrying 9.6 kips of tension (blue) because the beam is transferring the lateral force from brace M5 to M6.
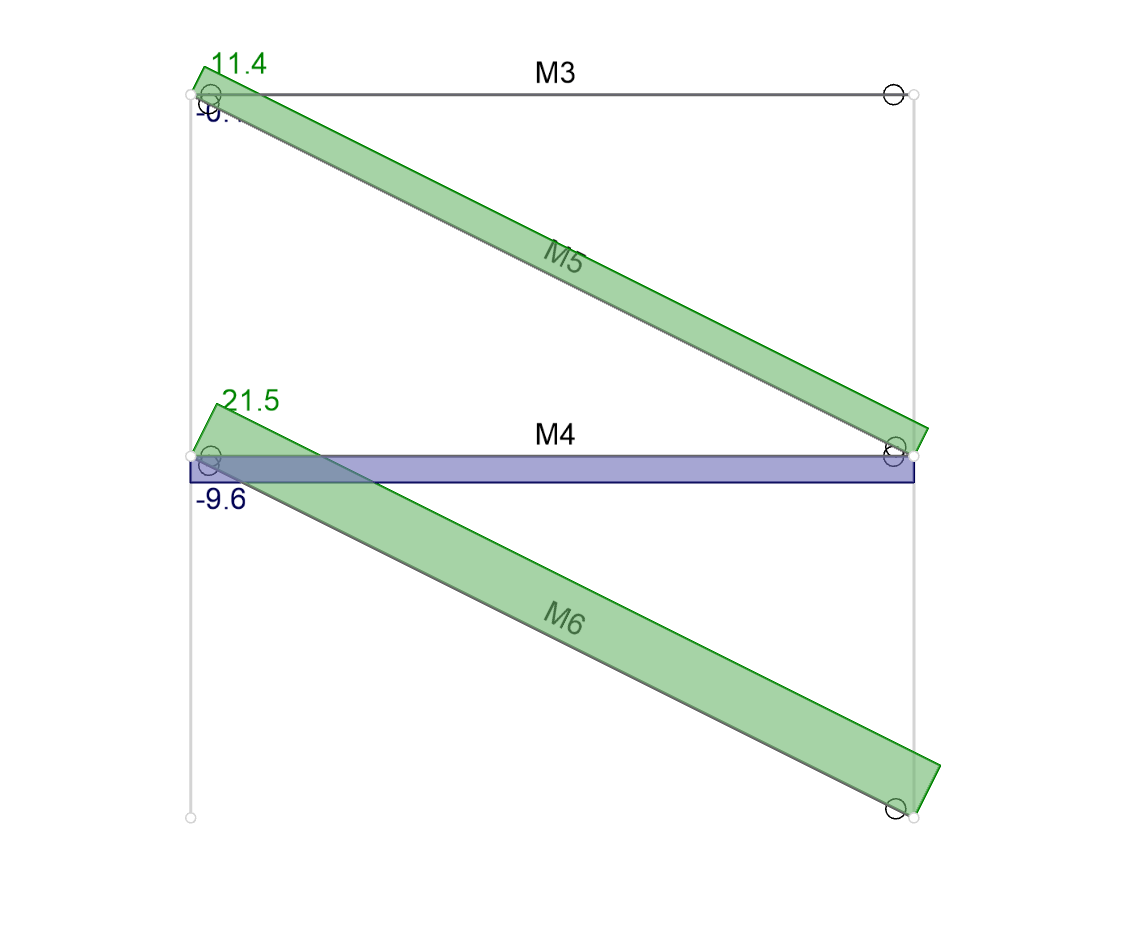
However, if a rigid diaphragm is created at the floor level then the axial force in M4 disappears:
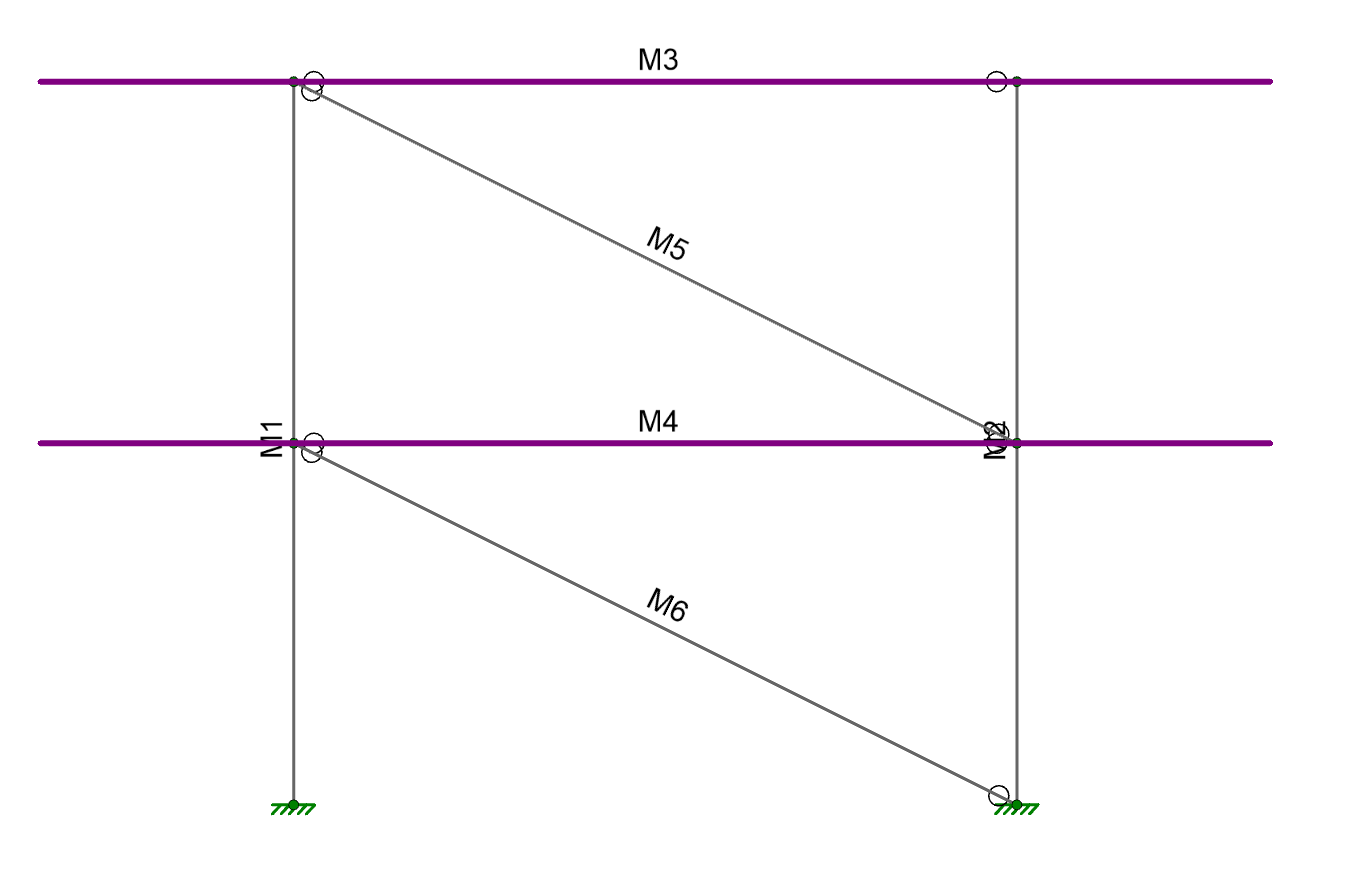
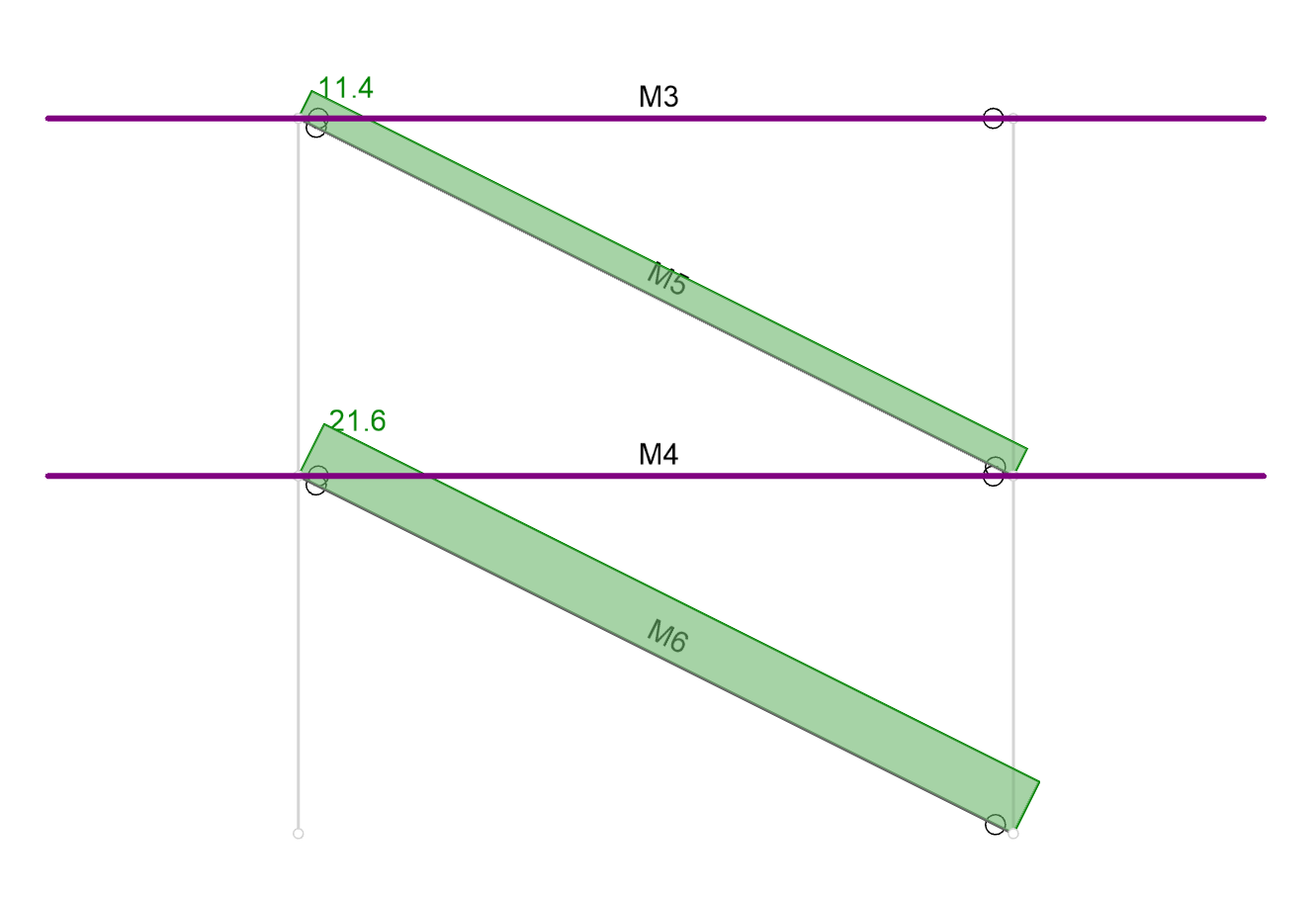
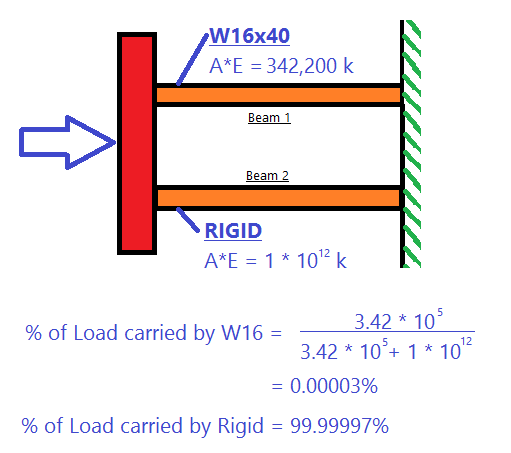
The question arises, how does the force now get from brace M5 down to brace M6? The answer is that the force is being carried entirely by the rigid diaphragm. See the image below, which explains why:
If the explanation above isn’t clear, another way to consider this problem is to look at the movement of nodes. In a rigid diaphragm, none of the nodes are allowed to get any closer or farther away from each other, regardless of the load applied. In the example below, the distance “x” is always the same number. If it wasn’t then the diaphragm must have deformed (shrunk) in the x direction, but it can’t deform or shrink if it is rigid.
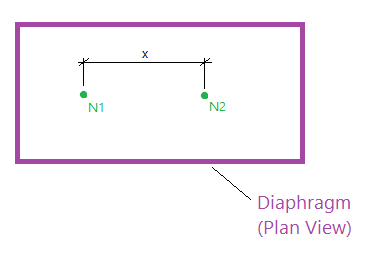
If a beam runs between nodes N1 and N2 (in the plane of the diaphragm) then the ends of that beam cannot move closer to each other. If the nodes cannot move closer to each other than the beam cannot have any axial deflection (shortening). If the beam does not shorten then it does not have any axial strain. If the beam does not have axial strain then it cannot have axial stress. If it does not have axial stress then we would not expect to see axial force.
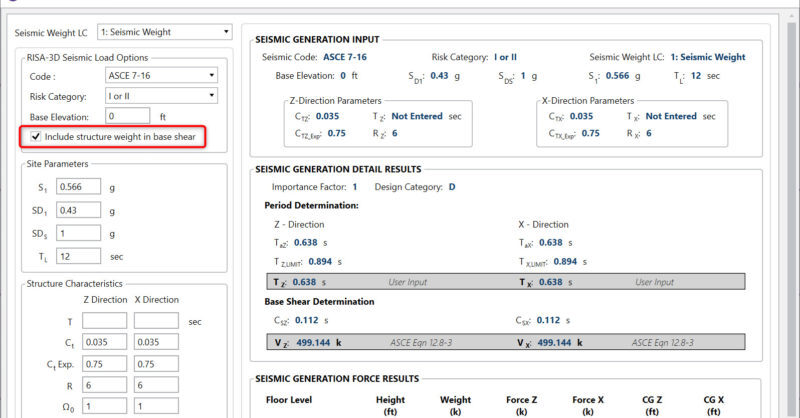
In the Seismic Loads dialog there is a checkbox for “Include structure weight in base shear”.
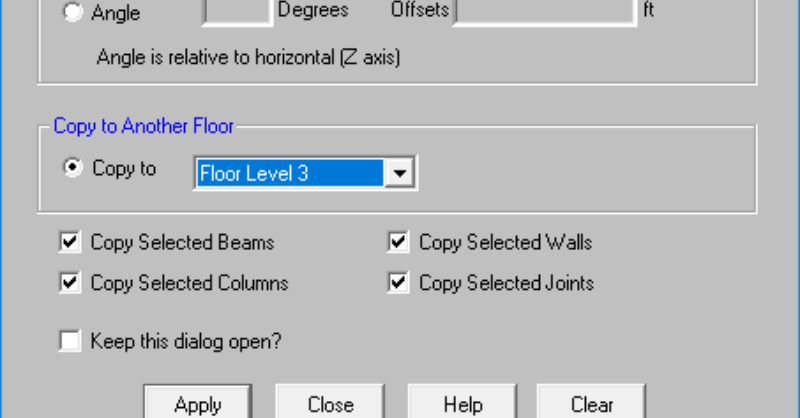
RISAFloor v13.0 now includes the added ability to graphically copy elements from one floor to another floor. This feature will expedite the...
RISAFloor v13 includes a variety of modeling features which allows users to quickly create and manipulate geometry. These features include...